Examples and Modelling
Learning Objective
Summarize the learner’s strengths and challenges using various information sources and complete the Summary of Results.
Context
Mrs. Cole, James’s resource teacher, collected the data for the selected domains.
Here are the data collected for the domain Daily Living Skills. These data will help Mrs. Cole to identify James’s strengths and challenges and thus set some learning objectives for him.
Here are the data collected for the domain Social Interaction Skills. These data will help Mrs. Cole to identify James’s strengths and challenges and thus set some learning objectives for him.
Mrs. Cole now prepares the Summary of Results. She compiles the results of the questionnaires, the interview, and the observation sessions. She also reviews the Functional Skills for Independence Screener report and adds relevant information to the Summary. She then consults James’s file and finds comments on his social skills written by his teacher from the year before.
See how Mrs. Cole completed James’s Summary of Results.
Example: Determine Intervention Priorities
Learning Objective
Determine intervention priorities, taking the suggested factors into consideration.
Context
Once the Summary of Results is completed, Mrs. Cole, the resource teacher, schedules a meeting with James’s collaborative team to present the Summary of Results to the members. The parents are especially curious to learn more about the results for Social Interaction Skills. Mrs. Cole provides them with details about this section of the assessment. Mrs. Brown, James’s teacher, thought that James’s challenges with eating and dressing were related to his motor skills (holding a fork, doing up a zipper), but she now realizes that it is more a matter of motivation and that distractions affect James’s performance.
Mrs. Cole talks with the other team members, who agree that the Summary of Results provides an accurate picture of James’s strengths and challenges. Taking this information into account, the team reviews each of the six questions suggested for determining the intervention priorities.
- Does the lack of certain skills pose a risk to the learner’s safety?
The team decides that none of the skill areas poses a risk to James’s safety.
- What skills are important for the learner’s health (e.g., basic hygiene, healthy eating habits, and physical activity)?
Certain eating and dressing skills have an impact on his healthy eating habits and physical activity.
- What skills are of interest to the learner?
James is interested in outdoor activities, and his challenges in dressing prevent him from fully participating in these activities.
- What were the priorities identified by the parents/guardians during the Screener?
The team members agree on the importance of social skills. Not only were these skills recognized by the parents as being an issue, but they may also provide James with more opportunities to participate in school and community life.
- What is the learner’s most significant barrier to learning the skills needed to participate in school, community, and family activities?
Social skills are essential for participating fully in school, community, and family activities.
- Which skills would enable the learner to achieve his post-secondary goals?
James is still very young, but the team believes that eating and dressing skills are essential for his independence. Social skills are important as well and help in building healthy, meaningful friendships.
Here are the skills recommended as highest priority by James’s collaborative team:
| Targeted Skills |
|---|
| Finish eating meals in a reasonable amount of time, despite distractions. |
| Put on his winter coat, mittens, and boots on his own, within a reasonable amount of time. |
| Initiate and continue a conversation with a same-aged peer. |
| Recognize and interpret non-verbal cues that indicate different emotions and react accordingly. |
Example: Select an Appropriate Intervention
Learning Objective
Choose an intervention from the evidence-based interventions suggested in the Intervention Selection Tool.
Context
At the same meeting, Mrs. Cole, James’s resource teacher, presents the Intervention Selection Tool to the members of the collaborative team. For each of the four targeted skills, the team answers the questions and agrees on a suggested intervention.
Click to see how James's team selected an appropriate evidence-based intervention for each of the four targeted skills:
Skill: Finish eating meals in a reasonable amount of time, despite distractions
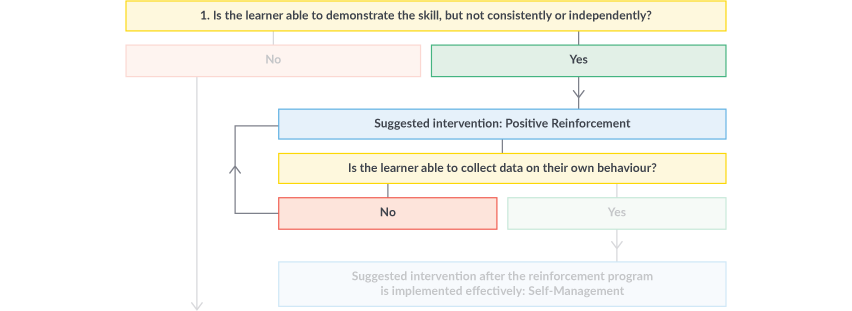
James can eat on his own, but he gets distracted, which slows him down. Positive reinforcement is therefore the recommended intervention for this skill.
Skill: Put on his winter coat, mittens, and boots on his own, within a reasonable amount of time

James can put on his coat, mittens, and boots at home. Positive reinforcement is therefore the recommended intervention for this skill.
Skill: Initiate and continue a conversation with a same-aged peer
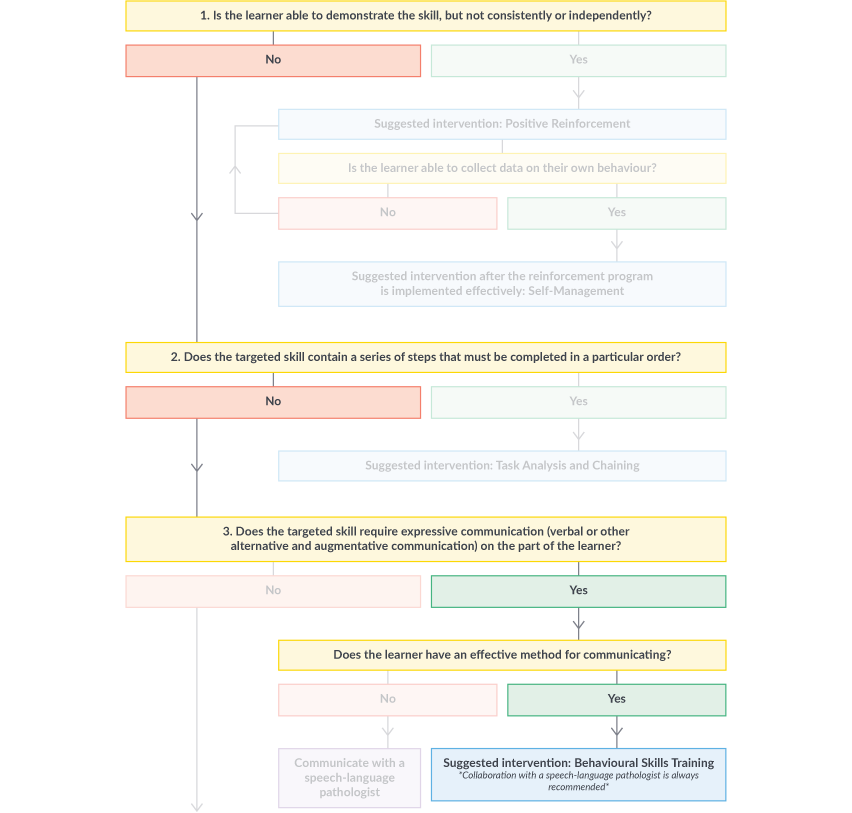
James can communicate orally and is not being seen by a speech language pathologist. Behavioural Skills Training is therefore the recommended intervention for teaching this skill.
Skill: Recognize and interpret non-verbal cues that indicate different emotions and react accordingly.

James can communicate orally and is not being seen by a speech language pathologist. Behavioural Skills Training is therefore the recommended intervention for teaching this skill.
